ASTM D695: End Loading Compression
The ASTM D695 standard describes the end loading compression test. The standard test method is used to determine the compressive properties of plastics and continuous fiber-reinforced composite materials.
This method is based on standard ASTM D695, which was originally developed for plastics testing, and was further developed for testing of continuous fiber-reinforced composite materials in standards DIN EN 2850 and Boeing BSS 7260 Type III and IV. The relatively simple test arrangement and a simple compression test kit, which includes a precisely vertically positioned anti-buckling support, are very beneficial.
The DIN EN 2850 (Type B) and Boeing BSS 7260 (Type III and Type IV) also describe the end loading compression test on composites.
End loading compression test to ASTM D695
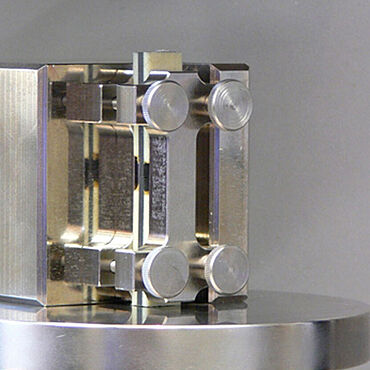
In the end loading compression test to ASTM D695, the specimen is loaded longitudinally between two compression platens. The anti-buckling device prevents premature failure through superimposed bending, however does not contribute to the force transmission into the specimen. The force is applied exclusively via the end faces of the specimen and therefore requires them to be processed precisely.
A specimen without cap strips is used to measure the compression modulus. To determine the validity of the compression test by quantifying superimposed bending deformations (percent bending), a strain measurement is carried out with separately measuring strain gauges applied centrally on both sides. Here, an anti-buckling support with recesses at the locations of the applied strain gauges is required. The signals of the strain gauges are then averaged for determination of the compressive strain.
To measure the compressive strength, a specimen with cap strips is used to increase the surface area for force application and achieve failure in the unsupported center section of the specimen. Failure in the loading points is an invalid failure mode and always leads to lower compressive strength values. Due to the very short length of the unsupported area of the specimen, the application of strain gauges for this type of specimen is relatively complex when compared with other compression test methods.
Generally, if the test is performed correctly, reproducible compressive modulus values are obtained, while the determination of compressive strength is often subjected to more scatter.
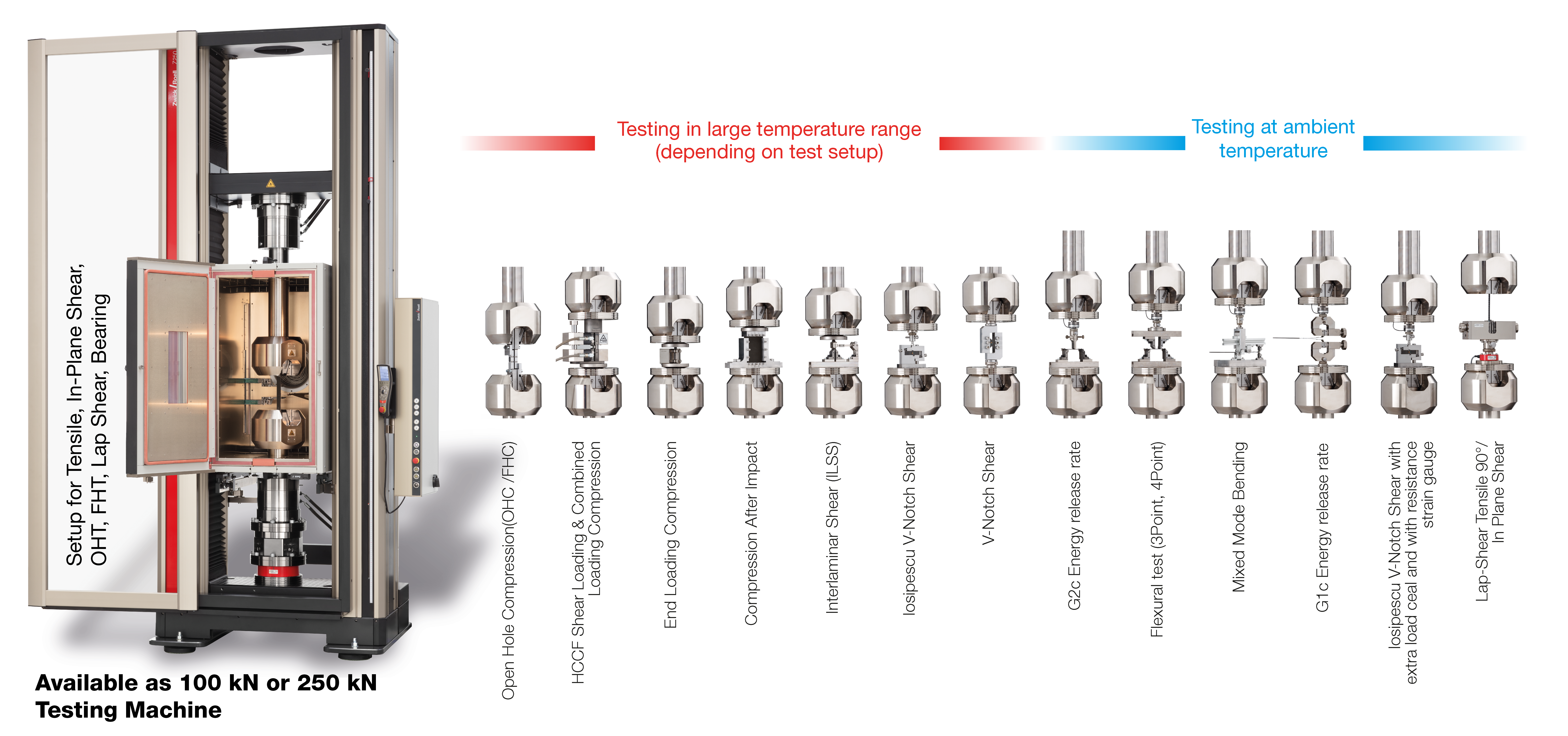
Modular testing system for composites
Larger testing laboratories with correspondingly high test volume use different testing machines for the very diverse composite testing methods, and can thereby minimize conversion efforts. The individual testing machines can be adjusted to the force range required for the various types of tests. If throughput rates are not high or consistent enough that an investment in multiple testing machines makes sense, an alternative option is to equip a single testing machine so that you can perform as many test methods as possible with the least amount of machine conversion effort.
ZwickRoell developed a modular design, which is available as a 100 kN or 250 kN testing machine covering 21 test methods and approximately 120 test standards (ISO, EN, ASTM, as well as Airbus AITM and Boeing BSS), and which allows for comprehensive characterization of fiber-reinforced composite materials at ambient temperature or for tests at low or high temperatures ranging from -80 °C to +360 °C.